Proper irrigation management provides adequate moisture to crops while helping keep water, soil sediments, and nutrients in the field.
Nitrate-nitrogen (NO3– – N) from fertilizer is extremely soluble and moves readily with irrigation water.
Phosphorus is relatively insoluble in water but is attached to soil sediments that may be carried away by irrigation water.
Irrigation Management Facts
- Irrigation scheduling is the decision of when and how much water to apply to a crop.
- The management goal is to match the timing and amount of irrigation water with crop moisture needs.
- Over-irrigation wastes water and energy and can result in nutrient losses to surface runoff and leaching below the root zone.
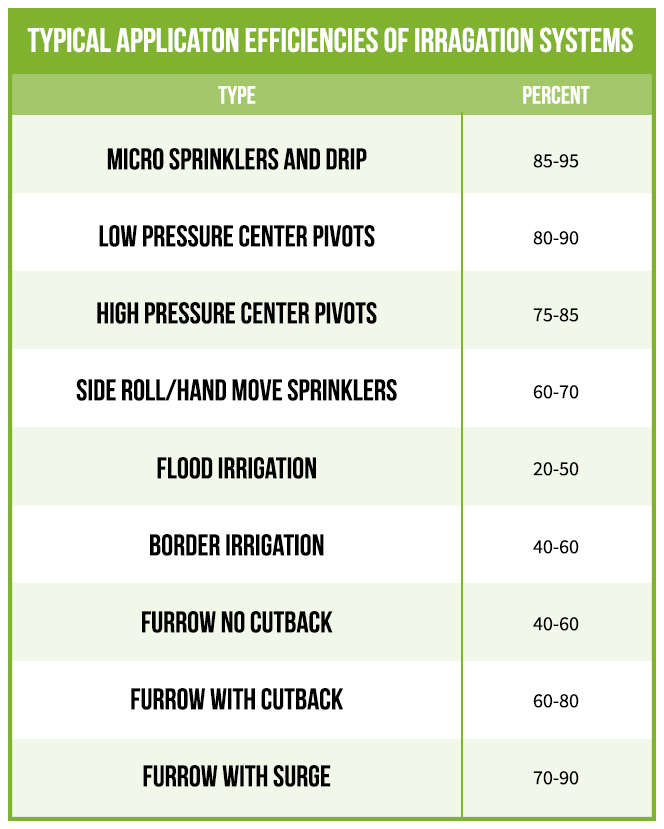
Irrigation System BMPs
- Install improved irrigation systems to improve irrigation efficiency and uniformity.
- Check and maintain irrigation systems regularly.
- Test sprinklers periodically for depth of application, pressure, and uniformity.
- Line irrigation water delivery ditches and install pipelines to convey water to reduce seepage losses.
Irrigation Scheduling BMPs
- Schedule irrigation based on plant or soil factors:
- Plant-based scheduling
- Visual appearance
- Canopy sensors
- Evapotranspiration estimation: weather stations; atmometers; remote sensing
- Soil-based scheduling
- Hand-feel
- Probes
- Sensors
- Plant-based scheduling
- Utilize irrigation scheduling tools
Resources
- CSU WISE Irrigation Scheduler
- Agricultural Water Conservation Clearinghouse
- CSU Water Quality Interpretation Tool
- Colorado High Plains Irrigation Guide
- Colorado Agricultural Meteorological Network and Crop ET Reports
- Crop Water Use and Growth Stages
- Effects of Weather on Irrigation Requirements
- Irrigation Ditches and their Operation
- Irrigation: Inspecting and Correcting Turf Irrigation System Problems
- Irrigation Pumping Plant Efficiency
- Irrigation Scheduling
- Irrigation Scheduling: The Water-Balance Approach
- Irrigation Water Quality Criteria
- Limited Irrigation Management: Principles and Practices
- Micro Sprinkler Irrigation for Orchards
- Nitrogen and Irrigation Management
- Seasonal Water Needs and Opportunities for Limited Irrigation for Colorado Crops
FAQ
What are best management practices (BMPs)?
Best management practices, or BMPs, are recommended structures, methods, and practices designed to protect water quality. BMPs can provide environmental, agronomic, and economic benefits.
The cost, economic return, ease of implementation, and overall effectiveness will vary from practice to practice. Recommended BMPs may include already widely accepted and utilized agricultural practices.
Every farm is unique and requires a particular combination of practices that meets the needs of the land and the producer.
Why is irrigation management important to managing nutrients and other water quality issues?
Proper irrigation management provides adequate moisture to crops while helping keep water, soil sediments, nutrients, and other chemicals in the field. Nitrogen and phosphorus can be soluble in water and carried away into surface water and groundwater.
What is irrigation uniformity?
A measure of how evenly irrigation water is applied across a crop area.

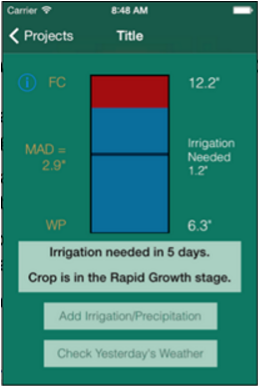 View wise.colostate.edu
View wise.colostate.edu